Daily Current Affairs - 22nd January 2026
- TPP

- Jan 22
- 17 min read
Updated: Jan 23
Comprehensive UPSC Current Affairs Summary | India’s 5-Layer AI Ecosystem at WEF 2026, Carney Doctrine for Middle-Power Multilateralism, Spain Joins IPOI, SIDBI Equity Infusion, Draft National Electricity Policy 2026, C-295 Aircraft, India’s First Private EO Satellite Constellation, Licence-Free 6GHz WiFi, WHO Health Tax Reports, APY Extension, Sukanya Samriddhi @11 Years, Lambada Tribe ST Status, Indira Gandhi Peace Prize 2025, Sukhatme National Award in Statistics and more.
If you missed Monthly Current Affairs Pointers (CAP) | Nov - Dec 2025, read it hereTable of Content
SECURITY / DEFENCE
India’s Comprehensive Approach to Artificial Intelligence – 5-Layer AI Ecosystem (WEF 2026)
On the sidelines of World Economic Forum (WEF) 2026, the Union Minister highlighted India’s comprehensive approach to Artificial Intelligence (AI).
The Minister explained that the AI ecosystem consists of five interlinked layers, enabling end-to-end AI development and deployment.
These layers include the application layer, the models layer, the semiconductor or chip layer, infrastructure such as data centres, and the energy layer.
Application and Usage Layer
The application and usage layer offers the highest Return on Investment (RoI), meaning it delivers maximum value relative to cost.
India aims to lead in applying AI to enterprise workflows, improving productivity and operational efficiency.
India is also focusing on public service delivery, using AI to enhance citizen-centric governance.
Kisan e-Mitra is an AI-powered chatbot designed to assist farmers with agricultural information and services.
Bhashini provides AI-based translation in more than 20 Indian languages, enabling access to digital services.
Model Layer
At the model layer, India is prioritising focused AI models instead of relying only on massive models.
India is developing around 12 specialised AI models tailored to specific use cases.
These models can run on small GPU clusters, which require fewer high-end computing resources.
Such models can deliver AI services at low cost to a very large population.
It was highlighted that nearly 95% of AI workloads today are handled by small models.
A 50-billion parameter model is considered sufficient for most enterprise requirements.
Semiconductor and AI Infrastructure Layers
At the semiconductor layer, India is focusing on indigenous custom silicon development to reduce dependency on imports.
Custom silicon refers to chips designed for specific applications to improve performance and efficiency.
India is focusing on manufacturing in the 28nm to 90nm range, which are mature and widely used semiconductor nodes.
These chips support applications such as electric vehicles, automobiles, railways, and industrial systems.
In the AI infrastructure layer, approximately USD 70 billion in AI infrastructure investment has already been confirmed.
This investment is currently being rolled out to strengthen data centres and computing capacity.
Energy Readiness Layer
The energy layer focuses on ensuring reliable and sustainable power for AI growth.
India is integrating green energy to sustainably power its expanding data centre footprint.
Data centres are facilities that store, process, and manage large volumes of digital data required for AI systems.
India has opened nuclear energy to private sector participation through the Shakti Act.
This initiative will help support the full AI stack, from computing infrastructure to long-term energy security.
Third Path Framework for a Reformed, Inclusive and Networked Multilateralism
The Canadian Prime Minister, in his speech at the World Economic Forum (WEF) 2026, outlined a new global agenda called the “Third Path”.
This agenda was proposed in the context of intensifying US–China rivalry and a fading rule-based international order.
The Third Path, also known as the Carney Doctrine, seeks an alternative to great-power dominance in global governance.
Core Idea of the Third Path (Carney Doctrine)
The Third Path emphasizes cooperation among middle powers to reshape global order.
It aims to bridge great-power rivalries by maintaining engagement with competing blocs.
This approach seeks to reduce zero-sum geopolitical competition, where one side’s gain is seen as another’s loss.
The framework promotes mediation and coalition-building among like-minded states.
Such mediation helps prevent smaller states from becoming collateral damage in conflicts between major powers.
The Third Path also seeks to revive and sustain multilateralism.
This is done by reinforcing rules-based cooperation at the global level.
It supports reform of multilateral institutions such as the UN, WTO, and WHO.
Other objectives include protecting sovereignty and promoting strategic autonomy of states.
It also focuses on addressing global challenges like climate change, pandemics, and cyber threats.
Key Principles Underpinning the Third Path
The Third Path is grounded in “value-based realism”, which combines ethical principles with practical policy choices.
Value-based realism defends core principles such as sovereignty, territorial integrity, and human rights.
At the same time, it recognizes incremental progress, meaning change occurs gradually.
It also acknowledges diverging national interests among partner countries.
This approach accepts that partners may have different value priorities, known as value differentials.
A crucial foundation of value-based realism is building domestic strength, including economic and institutional capacity.
The Third Path also follows a policy of “variable geometry”.
Variable geometry involves forming different coalitions for different issues, based on shared interests and values.
Examples of variable-geometry cooperation include the Schengen Area, the G7 grouping, and the Quad formation.
Relevance and Role of Middle Powers
The Third Path framework is especially relevant for middle powers, including India.
Great powers are often defined as countries with a permanent seat on the UN Security Council, namely China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
These great powers exert economic, political, and military dominance over the international system.
Middle powers are states below great powers that do not dominate the global system.
However, middle powers possess significant diplomatic, economic, technological, or normative influence.
Examples of middle powers include India, Canada, Australia, Japan, South Korea, Indonesia, Brazil, and several European Union countries.
Spain Joins the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI)
IPOI is a non-treaty-based voluntary arrangement, meaning participation is based on cooperation rather than legal obligations.
The initiative promotes a rules-based regional order in the Indo-Pacific region.
The Indo-Pacific is defined as an interconnected space between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
These two oceans are joined by the Malacca Strait, which is a major global trading channel.
The Indo-Pacific region is home to more than half of the world’s population.
It also accounts for nearly two-thirds of the global economy, highlighting its strategic importance.
About the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI)
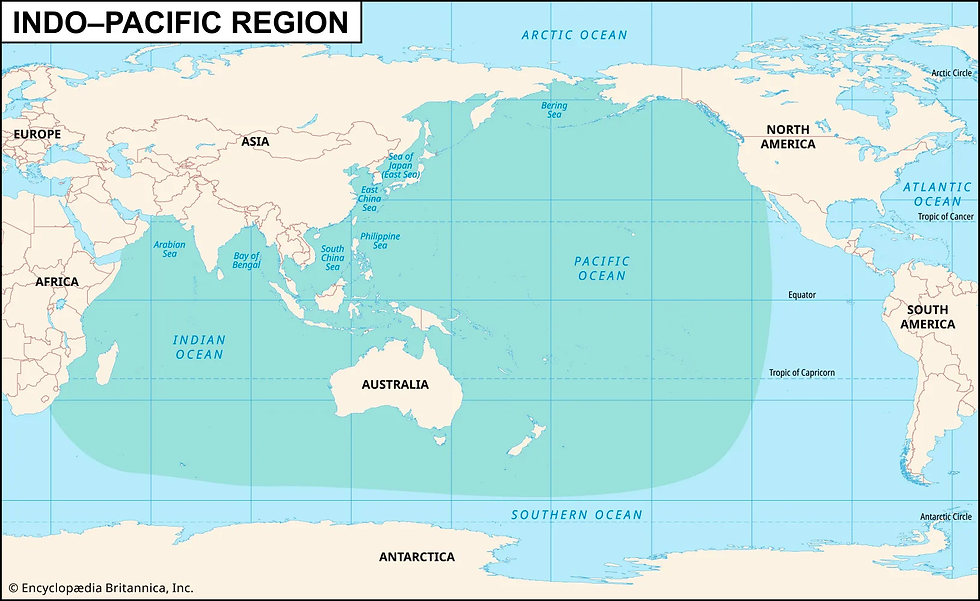
The Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI) was launched by India. It was launched at the East Asia Summit in 2019, which was held in Bangkok, Thailand.
IPOI builds upon the “Security and Growth for All in the Region” (SAGAR) initiative announced by India in 2015.
SAGAR encourages countries to cooperate and synergise efforts in the maritime domain.
The objective of SAGAR is to ensure a safe, secure, and stable maritime environment.
IPOI is structured around seven pillars for cooperation.
One key pillar is Maritime Security, which focuses on safety and stability at sea.
Another pillar is Maritime Ecology, which emphasizes protection of marine ecosystems.
Capacity Building and Resource Sharing is included to enhance maritime capabilities of participating states.
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management is another pillar, focusing on preparedness and response to maritime disasters.
Key Significance of IPOI
IPOI plays a role in countering China’s assertiveness in the Indo-Pacific region.
For example, in 2020, India and Vietnam agreed to enhance their bilateral cooperation in line with IPOI.
IPOI also shows convergence with other global and regional initiatives.
One such initiative is AIIPOIP, the Australia–India Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative Partnership.
It also aligns with AOIP, the ASEAN Outlook for the Indo-Pacific.
Other converging frameworks include the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF), strengthening regional cooperation.
Equity support of ₹5,000 crore to SIDBI
The Union Cabinet approved equity support of ₹5,000 crore to the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI).
Equity support refers to capital infusion by the government to strengthen an institution’s financial base.
About SIDBI
SIDBI was set up in 1990. It was established under the provisions of the Small Industries Development Bank of India Act, 1989.
SIDBI acts as the principal financial institution for the promotion, financing, and development of the MSME sector.
MSMEs refer to Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, which form the backbone of India’s economy.
SIDBI also serves as a nodal agency for various MSME-focused schemes.
A nodal agency is an institution responsible for coordination, implementation, and monitoring of government schemes.
Netting of Funds for Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs)
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) proposed netting of funds for Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) to improve market functioning.
This proposal aims to enhance operational efficiency, which means smoother and faster settlement of transactions.
It also seeks to reduce the cost of funding for FPIs, referring to the expenses incurred to arrange money for trades.
Netting of funds allows FPIs to use same-day sale proceeds to finance same-day purchases in the cash market, which is the segment where securities are traded for immediate settlement.
Under this system, FPIs are required to fulfil only the net fund obligation, meaning the difference between total purchases and total sales.
The main purpose of netting is to reduce liquidity pressure, which refers to the need to arrange large upfront funds.
It also helps in lowering funding costs, making market participation more efficient for FPIs.
As a safeguard, the netting facility applies only to outright transactions carried out by FPIs.
Outright transactions are those in which there is either a purchase or a sale, but not both, of a security.
These transactions must occur within a particular settlement cycle, which is the fixed time period for completing a trade and fund transfer.
Draft National Electricity Policy (NEP) 2026
The Draft National Electricity Policy (NEP) 2026 has been released by the Ministry of Power.
The Draft NEP 2026 is proposed to replace the existing National Electricity Policy notified in 2005.
The policy targets per capita electricity consumption of 2,000 kWh by 2030.
It further aims to raise per capita electricity consumption to over 4,000 kWh by 2047.
Key Achievements of India’s Power Sector
India achieved universal electrification in 2021, ensuring electricity access to all households.
The Unified National Grid has been operational since 2013.
This grid enables seamless power transfer across states, improving reliability and efficiency.
India’s per capita electricity consumption increased to 1,460 kWh in 2024–25.
Key Features of Draft NEP 2026
The policy introduces index-based annual tariff revision, linking tariffs to a suitable index.
This mechanism allows automatic annual revision of electricity tariffs.
The policy emphasizes cybersecurity in the power sector.
It proposes establishment of a robust cybersecurity framework for critical power infrastructure.
The policy mandates storage of power sector data within India, strengthening data sovereignty.
The Draft NEP proposes the establishment of a Distribution System Operator (DSO).
A DSO is an entity responsible for managing and operating the distribution network.
The DSO will facilitate network sharing among multiple users.
It will also enable integration of distributed renewable energy sources.
The framework supports energy storage systems and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) systems, where electric vehicles supply power back to the grid.
The policy promotes renewable energy generation and storage.
It encourages market-based deployment of energy storage solutions.
The policy also supports adoption of emerging Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) technologies.
Need for the Draft NEP 2026
One key need is ensuring the financial sustainability of DISCOMs.
DISCOMs, or Distribution Companies, have accumulated significant financial losses.
They also carry substantial outstanding debt, affecting sector stability.
The policy addresses the issue of non-cost-reflective tariffs.
Lack of cost-reflective tariffs creates revenue gaps and operational inefficiencies.
Another objective is boosting industrial competitiveness.
Cross-subsidisation has led to high industrial electricity tariffs.
High tariffs undermine the global competitiveness of Indian industry.
C-295 Transport Aircraft
India’s first “Made in India” C-295 transport aircraft is scheduled to roll out before September 2026.
The aircraft is being manufactured at the Airbus–Tata Final Assembly Line in Vadodara, marking a major defence manufacturing milestone.
About the C-295 Aircraft
The C-295 is a medium-range tactical transport aircraft, designed for versatile military operations.
It is powered by twin-engine turboprop systems, which provide efficiency and reliability.
The aircraft is an efficient tactical transport platform, suitable for varied mission profiles.
It has a flight endurance of up to 11 hours, enabling long-duration operations.
One of its key features is Short Take-Off and Landing (STOL) capability.
STOL allows the aircraft to operate from short and unprepared runways, enhancing operational flexibility.
India’s 1st Private EO Satellite Constellation
A Pixxel-led consortium has signed an agreement with IN-SPACe to design, build, and operate India’s first national private Earth Observation (EO) satellite constellation.
The Pixxel-led consortium comprises Pixxel, Piersight Space, Satsure Analytics India, and Dhruva Space.
The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) is India’s nodal agency for private space activities.
IN-SPACe authorises, regulates, and promotes private sector participation in space activities.
Key Features of the EO Constellation Project
The project will be executed under a Public–Private Partnership (PPP) model, which combines government oversight with private sector execution. The PPP framework will create a complete end-to-end Earth Observation ecosystem.
This ecosystem will cover satellite deployment, ensuring space-based data collection.
It will also include value-added geospatial analytics, enabling actionable insights from satellite data.
The EO constellation will consist of 12 satellites, forming a coordinated satellite network.
These satellites will provide very high-resolution optical imaging, enabling detailed surface observation.
They will also carry multispectral sensors, which capture data across multiple wavelengths.
The constellation will include Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), which enables imaging in all weather and day-night conditions.
Hyperspectral imaging will also be used to capture fine spectral signatures of Earth’s surface.
The project involves an investment of ₹1,200 crore. This investment will be spread over a 5-year period, indicating long-term commitment.
The project represents a strategic shift from government-built to industry-operated national EO infrastructure.
About Earth Observation (EO) Satellites
Earth Observation satellites monitor and collect data about the Earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere.
They use optical, multispectral, hyperspectral, and radar sensors to gather diverse datasets.
EO satellites have major applications in agriculture, including crop monitoring and yield estimation.
They are critical for disaster management, supporting early detection and response.
EO data is used in climate change studies, enabling long-term environmental monitoring.
These satellites support urban planning by mapping land use and infrastructure growth.
They also aid water resource management, including river basin and groundwater assessment.
EO satellites play an important role in national security through surveillance and reconnaissance.
Strategic Importance for India
The strategic value of EO satellites lies in supporting early warning systems for natural and human-made disasters.
They enable evidence-based policymaking through reliable geospatial data.
EO capabilities strengthen self-reliance in geospatial data, reducing dependence on foreign sources.
India’s major EO satellites include HySIS, which focuses on hyperspectral imaging.
Cartosat-3 provides high-resolution cartographic data.
RISAT-2B supports radar-based Earth observation.
EOS-07 is another key satellite contributing to India’s EO capabilities.
WiFi (Wireless Fidelity)
The government has allowed the licence-free use of a portion of the high-speed 6GHz spectrum crucial for providing high-speed WiFi.
About WiFi
WiFi allows devices to connect to the internet without cables.
It transmits data using radio waves over specific frequency bands.
On the other hand, Lifi (Light Fidelity) uses light as the medium for high-speed data transmission and is several times faster than 'WiFi'.
Benefits: Provides flexible, reliable, and high-speed internet access.
WHO Global Reports on Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Taxes and Alcohol Taxes
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) released two global reports on the use of sugar-sweetened beverage taxes and alcohol taxes.
These reports focus on health taxes, which are fiscal measures imposed on harmful products to improve public health.
Impact of Health Taxes on Public Health and Revenue
A major finding is that health taxes reduce consumption of harmful products, such as sugary drinks and alcohol.
Reduced consumption helps prevent Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs), which are long-term diseases not spread by infection.
These NCDs include obesity, which refers to excessive body fat accumulation.
Diabetes, a disease affecting blood sugar regulation, is also impacted.
Cancer, caused by uncontrolled cell growth, is another NCD influenced by lower consumption.
Cardiovascular diseases, which affect the heart and blood vessels, are similarly reduced.
Mental disorders linked to alcohol consumption are also addressed through health taxation.
The reports highlight that health taxes generate additional government revenue.
This revenue can be invested in the health sector, strengthening public healthcare systems.
Evidence from Country Experience
The reports present a case study of the United Kingdom to illustrate effective taxation.
The UK introduced a tax on sugary drinks in 2018 as a public health intervention.
This policy resulted in reduced sugar consumption.
It also contributed to lower obesity levels.
At the same time, the tax led to increased government revenue.
Key Challenges in Alcohol and Sugary Drink Taxation
The reports note rising real affordability of alcohol in many countries.
Real affordability means alcohol has become cheaper relative to people’s incomes.
Although most countries tax alcohol, tax rates are not regularly adjusted for inflation.
Alcohol taxes are also not aligned with income growth, reducing their long-term effectiveness.
The reports identify tax gaps in sugar-sweetened beverages.
Carbonated drinks are generally taxed as sugary beverages.
However, 100 percent fruit juices often escape taxation despite high sugar content.
Sweetened milk products are frequently excluded from tax coverage.
Ready-to-drink coffees and teas also remain untaxed in many countries, creating loopholes in health tax policies.
First state-funded BSL-4 Containment Facility and laboratory in Gandhinagar
The Home Minister laid the foundation stone of the first state-funded BSL-4 Containment Facility and laboratory in Gandhinagar, strengthening India’s high-end biosecurity capacity.
Concept of Bio-Safety Levels (BSL)
Bio-Safety Levels (BSL) are graded laboratory safety safeguards designed for handling biological agents.
These safeguards aim to protect laboratory personnel working with infectious materials.
BSL measures also ensure the safety of the surrounding environment and community from accidental exposure.
There are four internationally recognized Bio-Safety Levels, classified from BSL-1 to BSL-4 based on risk intensity.
Lower and Moderate Bio-Safety Levels
BSL-1 is meant for low-risk agents, which pose little or no threat of infection in healthy adults.
BSL-1 laboratories follow basic laboratory practices for routine safety.
Standard Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as gloves and lab coats, is used in BSL-1 settings.
BSL-2 is designed for moderate-risk agents that can cause human disease but are manageable.
BSL-2 laboratories have restricted access to limit exposure.
Biosafety cabinets are used in BSL-2 labs to prevent the spread of infectious aerosols.
Enhanced PPE is required in BSL-2 laboratories for additional protection.
High and Maximum Bio-Safety Levels
BSL-3 is used for high-risk airborne pathogens capable of causing serious illness.
BSL-3 laboratories maintain controlled airflow to prevent pathogen escape.
These labs are sealed structures designed for maximum containment.
Personnel working in BSL-3 labs require advanced PPE.
BSL-4 laboratories handle highly dangerous and exotic microbes.
Infections caused by BSL-4 pathogens are often fatal, indicating extreme biological risk.
Such infections usually have no available treatment, making strict containment essential.
Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
The Union Cabinet approved the continuation of the Atal Pension Yojana (APY) till 2030–31, reaffirming the government’s commitment to social security.
About Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
Atal Pension Yojana (APY) was launched on 9th May, 2015.
The objective of APY is to create a universal social security system in India.
The scheme places special focus on the poor, under-privileged, and workers in the unorganised sector.
Eligibility under APY includes any citizen of India between 18 and 40 years of age.
Eligible subscribers must be non-income tax payers.
APY is a Central Sector Scheme, meaning it is fully funded and administered by the Central Government.
Key Features and Performance
APY offers a guaranteed minimum pension, ensuring income security in old age.
The pension ranges from ₹1,000 to ₹5,000 per month, depending on contributions made during the working years.
The pension becomes payable from the age of 60 years.
The scheme has enrolled over 8.66 crore subscribers across the country.
This wide coverage has made APY a cornerstone of India’s inclusive social security framework.
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY)
The Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) has completed 11 years since its launch, highlighting its sustained role in girl child welfare.
The scheme was launched as part of the Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao campaign, which focuses on protecting, educating, and empowering the girl child.
About Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY)
SSY was launched on 22nd January 2015 under the Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao initiative.
The objective of SSY is to promote the welfare of the girl child in India.
The scheme also aims to create a long-term savings corpus for education and future needs of the girl child.
Key Features of the Scheme
Eligibility under SSY is limited to a girl child below 10 years of age.
Only one SSY account is permitted per girl child, ensuring targeted benefits.
A family can open SSY accounts for a maximum of two girl children.
The scheme allows an annual deposit ranging from ₹250 to ₹1.5 lakh.
These deposits must be made for a period of 15 years.
The SSY account is operated by the guardian until the girl child attains 18 years of age.
The account matures after 21 years from the date of opening.
A partial withdrawal of up to 50% of the balance is allowed for educational purposes after 18 years of age.
Lambada Tribe
The Supreme Court of India is once again examining the long-standing dispute over the Scheduled Tribe (ST) status of the Lambada community in Telangana.
Scheduled Tribe (ST) status provides constitutional safeguards and affirmative action benefits to historically disadvantaged tribal communities.
Identity and Distribution
The Lambada tribe is also known as Sugalis or Banjaras.
They are one of the Scheduled Tribe communities in India.
The community is primarily spread across Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
Origin and Traditional Occupation
The Lambadas are believed to have originated from the Marwar region of Rajasthan.
Traditionally, they followed a semi-nomadic lifestyle.
Their traditional occupation involved transporting goods over long distances.
With the advent of British rule, they were compelled to give up this occupation due to changes in transport systems and regulations.
Language and Culture
The language spoken by the Lambada tribe is known as “Gor Boli” or “Lambadi”.
The community has a distinct cultural identity, reflected in its customs and traditions.
Traditional dress and rich embroidery are key features of Lambada culture.
Their cultural expression also includes traditional music performed using instruments such as the Dappans.
Sukhatme National Award in Statistics
The Government has invited nominations for the Sukhatme National Award in Statistics, highlighting its importance in the statistical domain.
The Sukhatme National Award in Statistics is instituted by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
The primary aim of the award is to recognize individual contributions through high-quality research work.
This research work should contribute to the improvement of the system of official statistics, which refers to government-generated data used for policymaking.
The award carries a formal citation, which is an official written recognition of achievement.
It also includes a shawl, symbolising honour and respect in Indian tradition.
A memento is awarded as a permanent token of recognition.
The award is given in alternate years, meaning it is not conferred annually.
The award has been conferred since the year 2000, marking its long-standing significance.
Eligibility for the award is restricted to Indian statisticians, ensuring national representation.
Eligible candidates must be 45 years of age or above at the time of consideration.
The award recognises lifetime contributions and achievements, indicating long-term impact in the field.
These contributions must be specifically in the field of Statistics, which involves the collection, analysis and interpretation of data.
Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development
Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development for 2025 awarded to human rights activist Graca Machel of Mozambique.
About Indira Gandhi Peace Prize
Instituted in 1985 and administered by the Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust.
It awarded annually to a person or organization without any distinction of nationality, race or religion, in recognition of creative efforts towards:
Promoting international peace and disarmament, racial equality, and goodwill and harmony among nations.
Securing economic co-operation and promoting a new international economic order.
Ensuring that the discoveries of science and modern knowledge are used for the larger good of the human race; and
Enlarging the scope of freedom and enriching the human spirit.
Kaladi
Under the One District One Product (ODOP) initiative, the GI-tagged Kaladi cuisine will be technologically upscaled.
Technological upscaling aims to develop diverse value-added food products while preserving traditional identity.
A Geographical Indication (GI) tag recognises products with unique qualities linked to a specific region.
About Kaladi
Kaladi is a traditional Dogra cuisine.
It originates from the Udhampur district of Jammu and Kashmir.
Kaladi is a very dense variety of cheese.
Nature and Serving Style
The dish is sautéed in its own fat, which enhances its flavour and texture.
It is salted before serving, adding to its characteristic taste.
Kaladi is served hot, typically accompanied by bun slices.
Traditional Preparation Method
Kaladi is traditionally prepared from raw full-fat milk.
Whey water is used as a coagulant, which helps in curdling the milk to form cheese.

Comments