Release of SDG Publications on 19th Statistics Day
- TPP

- Jun 29, 2025
- 4 min read
Updated: Jun 30, 2025

On the occasion of the 19th Statistics Day, celebrated on 29th June 2025, the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) released a set of important publications focused on tracking India’s progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These publications, rooted in data and analysis, reaffirm India’s commitment to aligning its national priorities with global development objectives.
The three key publications launched by MoSPI are:
Sustainable Development Goals – National Indicator Framework Progress Report, 2025
Data Snapshot on Sustainable Development Goals – National Indicator Framework, Progress Report, 2025
Sustainable Development Goals – National Indicator Framework, 2025
These documents are part of MoSPI’s annual tradition of releasing updated SDG reports every Statistics Day (29th June), based on the National Indicator Framework (NIF). Developed in collaboration with line Ministries, UN agencies, and other stakeholders, the NIF is a comprehensive national framework for monitoring the progress of the 17 SDGs and their targets through 284 national indicators. The aim is to support evidence-based policymaking by providing reliable and timely data.
The flagship report—Sustainable Development Goals – National Indicator Framework Progress Report, 2025—presents time series data collected from respective data source Ministries. It is structured into four core sections:
Overview and Executive Summary, detailing MoSPI’s role in coordinating national SDG monitoring and a goal-wise progress summary;
Data Snapshot, offering a visual summary of national indicator data;
Metadata, which explains each indicator in detail—covering the associated SDG goal, target, level and type of disaggregation, mapping with global indicators, unit of measurement, and data source;
Data Tables, which provide downloadable data (in Excel format) for each indicator.
The other two publications are concise, handbook-style documents derived from the main progress report:
The Data Snapshot offers a compact version of national-level time series data for SDG indicators.
The Sustainable Development Goals – National Indicator Framework, 2025 outlines all 284 national indicators, along with details of their data sources and frequency of data collection (periodicity).
These publications are made freely accessible to the public via the official MoSPI website (www.mospi.gov.in), in alignment with the Ministry’s commitment to transparency and data-driven governance.
Must Read
Key Highlights from the 2025 SDG NIF Progress Report
The 2025 report offers valuable insights into India’s performance across multiple dimensions of sustainable development. Here are some of the notable data-driven achievements:
Social Protection: The population covered by social protection systems/floors increased significantly from 22% in 2016 to 64.3% in 2025, reflecting broader access to safety nets such as pensions, maternity benefits, and health coverage.

Agricultural Productivity: The Gross Value Added (GVA) in agriculture per worker rose from ₹61,247 in 2015-16 to ₹94,110 in 2024-25, indicating rising productivity and incomes for farmers.

Access to Drinking Water: The share of the rural population using improved drinking water sources rose from 94.57% in 2015-16 to 99.62% in 2024-25, nearing universal coverage.

Renewable Energy:
The renewable energy share in total installed electricity generation grew from 16.02% in 2015-16 to 22.13% in 2024-25.

The installed renewable energy capacity rose from 64.04 watts per capita in 2014-15 to 156.31 watts per capita in 2024-25, reflecting a strong policy push toward clean energy.

Waste Management:
The number of waste recycling plants increased from 829 in 2019-20 to 3,036 in 2024-25.

The percentage of waste processed surged from 17.97% in 2015-16 to 80.7% in 2024-25, indicating major improvements in solid waste management infrastructure.

Start-up Ecosystem: The number of start-ups recognised under the Start-up India scheme rose dramatically from 453 in 2016 to 34,293 in 2024, showcasing vibrant entrepreneurial growth.

Income Inequality: The Gini coefficient—a common measure of income inequality—showed positive change:
In rural areas, it declined from 0.283 in 2011-12 to 0.237 in 2023-24.
In urban areas, it fell from 0.363 to 0.284 in the same period, indicating more equitable income distribution.

Emissions Intensity: India achieved a 36% reduction in emissions intensity of GDP in 2020 compared to 2005, signifying progress toward a low-carbon economy.

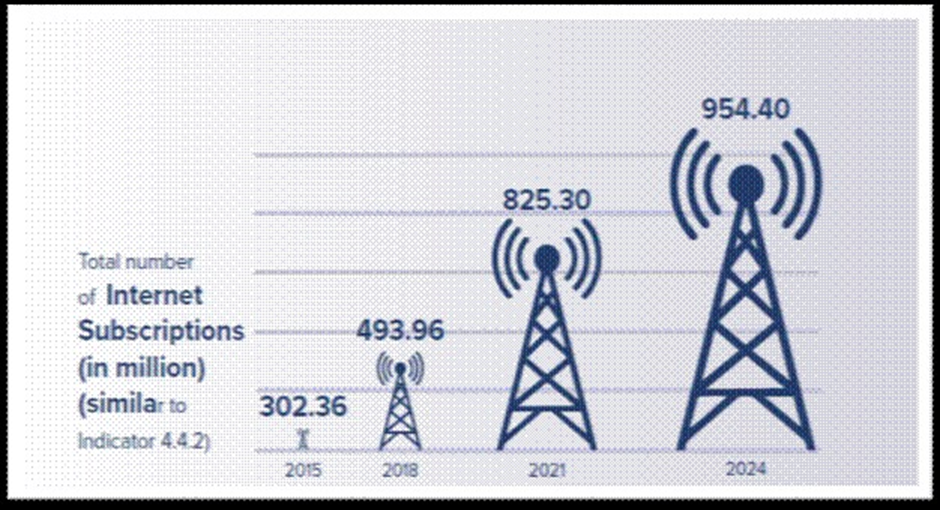
Digital Connectivity: The number of internet subscriptions rose from 302.36 million in 2015 to 954.40 million in 2024, reflecting deepening digital inclusion.
Forest Cover: India’s forest cover as a share of total geographical area increased modestly from 21.34% in 2015 to 21.76% in 2023, indicating sustained afforestation efforts.

Together, these reports provide a data-rich overview of India’s achievements and remaining challenges in implementing the Sustainable Development Goals. They offer a critical foundation for informed decision-making by policymakers, researchers, development agencies, and citizens committed to building a more sustainable and equitable future.
Click for UPSC Content
Click for Daily Quotes:
Stay updated with the latest news by joining our Telegram channel – The PRESS Pad , and follow us on Instagram and X.



Comments